The first human habitation in the Japanese archipelago has been traced to prehistoric times.The Jōmon period, named after its “cord-marked” pottery, was followed by the Yayoi in the first millennium BC, when new technologies were introduced from continental Asia. During this period, the first known written reference to Japan was recorded in …

replica of Heian period procession The Heian Period (794-1185) began with the Imperial family taking up residence in Heian (Kyoto) in 794. Towards the end of the Nara Period (710-794), when Japan was wracked by rebellions and upheaval, the capital was moved from Nara to Nagaoka in 784 by the

Heian period: Heian period, in Japanese history, the period between 794 and 1185, named for the location of the imperial capital, which was moved from Nara to Heian-kyō (Kyōto) in 794. The Chinese pattern of centralized government that was first adopted in the Nara period (710–784) gradually changed as the
The Heian Shrine (平安神宮, Heian-jingū) is a Shinto shrine located in Sakyō-ku, Kyoto, Japan.The Shrine is ranked as a Beppyō Jinja (別表神社) (the top rank for shrines) by the Association of Shinto Shrines.It is listed as an important cultural property of Japan.


Over its long history, Japanese art absorbed many foreign artistic traditions and carried on intermittent exchanges with China and Korea.When Japan came into contact with the Western world during the 19th century, Japanese woodblock prints, paintings and ceramics had a considerable influence on European art, particularly on cubism and …




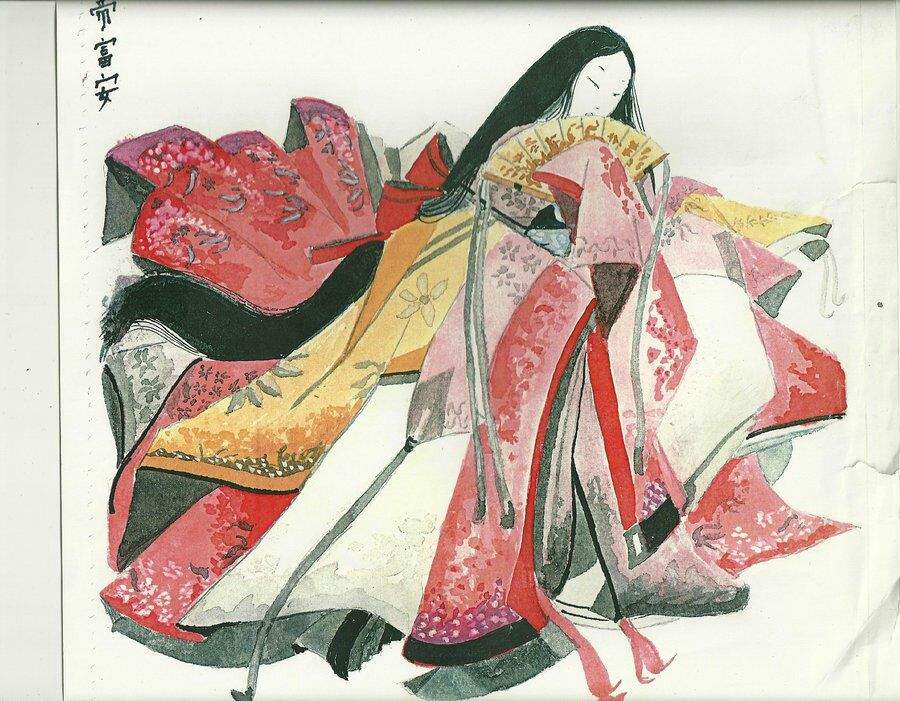
The Heian Period. teen of the noble family in formal dress called “kazami.” teen in everyday wear called “kazami.” Courtier in regular court dress, ikan: ho (=outer robe) and sashinuki
Famous Busshi (Sculptors) of Buddha Statues in Japan. Heian Era. Jocho, Enpa & Inpa colleges, Styles of Japanese Buddhist Statuary & Art.
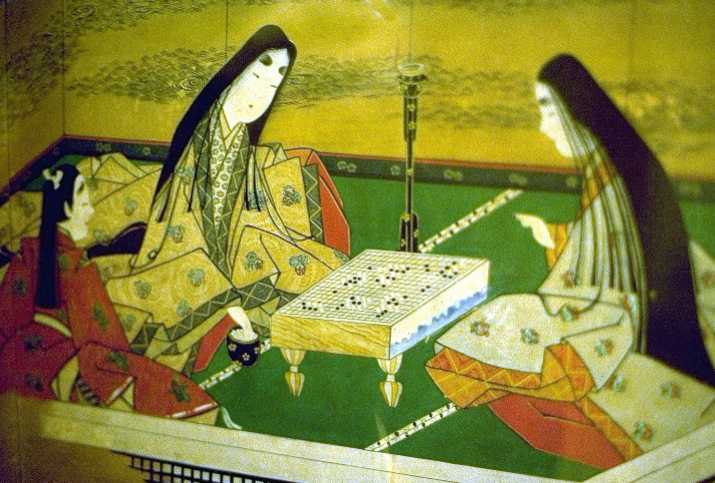
Chapter Three. The Heian Period Aristocrats. Japanese aristocratic society developed to its fullest extent during the long Heian period (794-1191).
Heian (“Hey-on”) Japan was the high point of Japanese aristocratic culture, a golden age of peace and harmony. The attitudes and aesthetic of court life established in this period continued many years after the emperor and his court lost power to the warring samurai.
Early Buddhism in Japan. Introduction of Buddhism and Buddhist Sculpture in Japan, from the Asuka, Nara, and Heian Periods.
